Economic Update for Nigeria: Mid-June 2024
As of mid-June 2024, Nigeria is experiencing significant economic volatility, marked by persistent inflation, labour unrest, and currency devaluation. The economic landscape is largely influenced by domestic policy decisions, ongoing labour disputes, and external economic pressures.
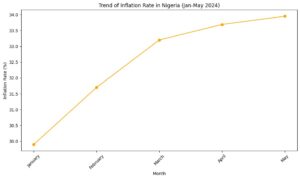
Inflation Trends: Nigeria’s inflation rate has continued to rise, reaching 33.95% in May 2024, a slight increase from 33.69% in April. This steady climb in inflation is fuelled by rising costs in food, housing, transportation, and energy sectors. The year-on-year inflation rate has significantly outpaced the previous year’s, indicating a deepening cost of living crisis.
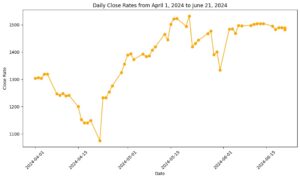
Stable FX Rate: Notably, the foreign exchange rate has shown signs of stability in June 2024 despite ongoing economic challenges. This stability could be attributed to temporary market adjustments which may have temporarily eased pressures on the naira.
Labor Market and Strikes: The trade unions have been particularly active, with nationwide strikes initiated in early June disrupting essential services, including power and air travel. These strikes stem from demands for substantial wage hikes in response to the soaring cost of living, with the government offering a far lower increase than the unions demand.
Government Policy and Economic Reforms: President Bola Ahmed Tinubu’s administration faces critical challenges, including managing the backlash from economic reforms such as the naira devaluation and the removal of fuel subsidies. These policies, intended to stabilize the economy, have so far exacerbated inflationary pressures and heightened public discontent.
Currency and Foreign Investment: The naira’s devaluation has failed to attract the expected level of foreign investment. Instead, it has increased the cost of imports, contributing to domestic price rises and further inflating the general price level. This has had a knock-on effect on the cost of living, particularly impacting food and essential goods prices.
Outlook: The near-term economic outlook for Nigeria remains precarious, with high inflation expected to persist if current trends continue. The government’s ability to negotiate with labour unions and stabilize the naira will be crucial in mitigating further economic deterioration. Additionally, enhancing domestic production and reducing import dependency are vital for long-term economic stability and growth.
Conclusion: Mid-June 2024 finds Nigeria at a critical juncture, facing profound economic challenges that require decisive action and comprehensive policy overhauls to stabilize the economy and address the pressing needs of its population.

